More Guides
Unraveling the Mystery: Is 3D Printing Food Safe?
Given the extensive use of 3D printing, safety, specifically food safety, has become a concern. Can these printed items be cleaned adequately to be safe for food handling or medical use? If a 3D printed prosthetic or utensil comes into contact with food, can it be cleaned to a level that prevents bacterial growth or contamination? Is it safe for kids to bite or chew on 3D printed objects?
After conducting comprehensive research and tests, it appears the answer is YES – 3D printed items can be sanitized to a food-safe level.
When is 3D Printing Food Safe?
What is Food Safe?

Before delving deeper, let’s break down a few key terms essential to understanding the concept of food safety in the context of 3D printed objects.
Firstly, when we say something is “food grade,” it denotes that the material is safe for human consumption or it’s approved to be in contact with food. “Food safe,” on the other hand, means that a food-grade material is also safe under the conditions of its intended use and won’t pose a food safety hazard.
Consequently, 3D printed items are indeed safe for the storage of dry foods and generally safe for short-term contact with food, as long as they are properly cleaned (see below). It’s crucial to mention that the cleaning process should be thorough. For best results, “wash, rinse, sanitize in bleach water” should be the mantra. This involves washing the part in warm soapy water, rinsing with warm water, and then soaking in a cold bleach bath for about 2 minutes.
Key Considerations for Ensuring Food Safety in 3D Printing
Bacteria Buildup

A 3D printed object can potentially become a breeding ground for bacteria in a matter of weeks. Despite certain materials being dishwasher-safe, harmful bacteria such as E. coli and salmonella may survive in the tiny crevices. Moreover, certain toxic molds find favorable conditions on several types of plastic and are difficult to eliminate. Cleaning with bleach or microwaving your polymer-based items are not viable options for germ removal.
For single-use items, bacteria build-up may not pose a significant issue. However, if your intent is to create a 3D printed object for prolonged usage, it’s strongly advised to utilize a food-safe coating to ensure safety and hygien
Food Safe Coatings and Sealants
To mitigate particle migration and bacterial buildup on 3D printed parts, applying a food-grade epoxy or polyurethane resin (must be 100% cured), or FDA approved PTFE (Teflon®), is advisable. This seals the surface, providing an extra safety barrier.
However, keep in mind that coatings may degrade over time and aren’t always dishwasher safe. Consequently, they don’t assure prolonged food safety, revealing the original potentially unsafe surface.
Cleaning Methods (IPA, Soap & Water)
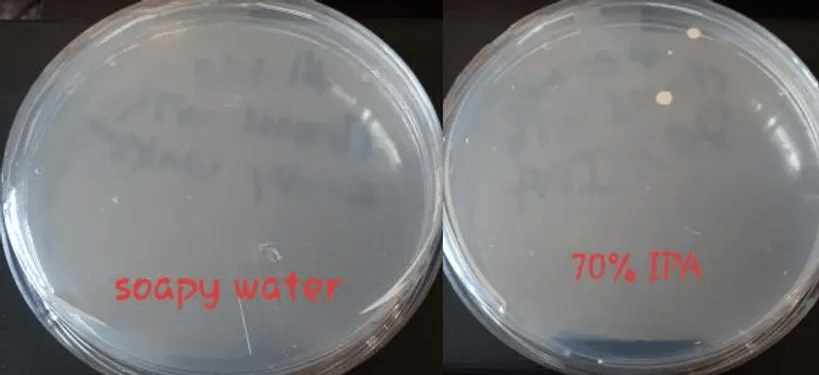
Various cleaning methods were tested, including hand washing with soap, disinfection with isopropyl alcohol (IPA), and the traditional wash-rinse-sanitize method used in food establishments. Tests were performed on a variety of materials (PLA+, PLA, PETG) and different objects such as respirator masks, utensils, and even hands.
Interestingly, the centuries-old practice of hand washing proved to be incredibly effective. If cleaned correctly with warm soapy water and then rinsed, 3D printed items showed no signs of harmful bacterial growth or contamination.
Is it Safe for Kids to Play with and Bite 3D Printed Models?

The safety of 3D printed toys depends on both the materials used and the post-processing. Some plastics like ABS can release harmful substances and are not suitable for children’s toys. However, others like PLA, derived from natural sources, are generally considered safer.
Yet, even with safer materials, 3D printed items often have grooves and cavities that can harbor bacteria. Therefore, it’s crucial to thoroughly clean and regularly check these toys for wear and tear. While steps can be taken to make 3D printed toys safer, adult supervision is always recommended, especially when children might put these objects in their mouths. With proper precautions, 3D printed toys can be both fun and safe for children.
FDM vs Resin in Food Safe
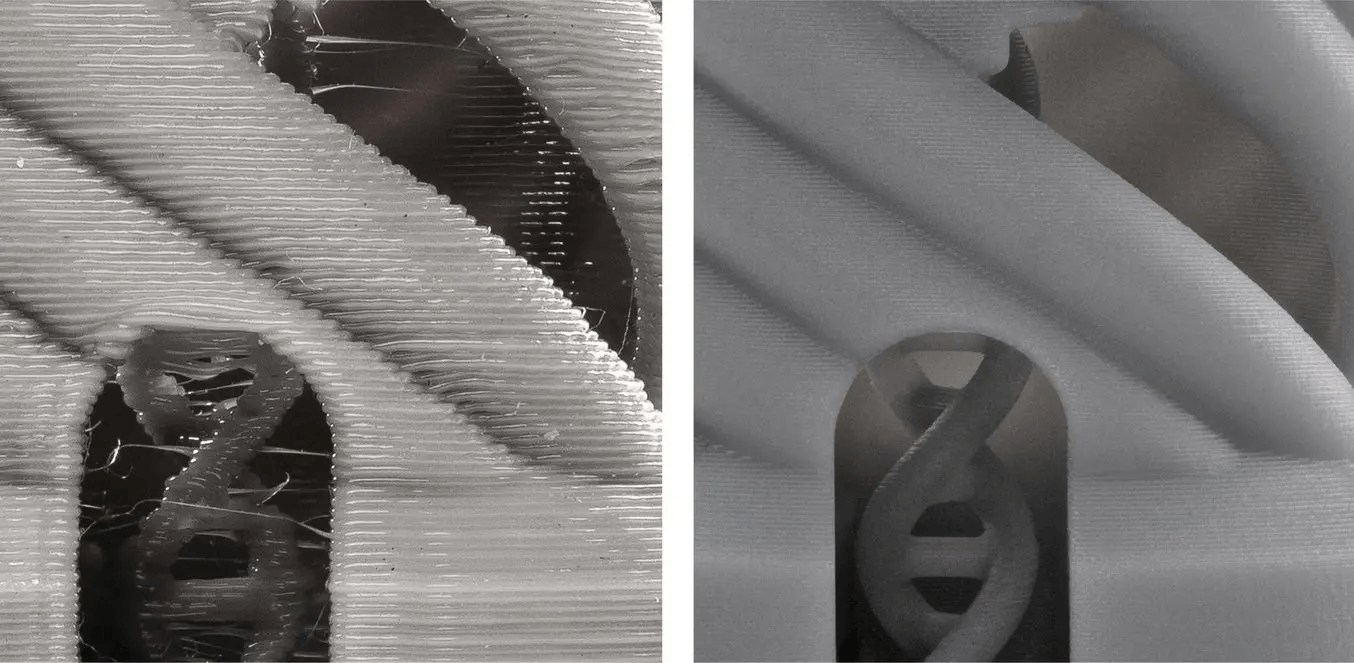

FDM Safety
The primary challenge with FDM parts, then, is preventing bacterial accumulation. As demonstrated in the above picture, FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) presents thicker layer lines compared to resin printing, leading to an increased potential for bacterial buildup. Hence, FDM-produced objects can become more susceptible to contamination.
For long-term food safety, FDM 3D prints need to possess a smooth surface. Chemical smoothing, using solvents like acetone, d-Limonene, or ethyl acetate, can eliminate many print irregularities, giving a smooth, glossy finish. Nevertheless, a subsequent application of a food-safe coating is still strongly recommended.
Resin Safety
While FDM has its unique set of challenges, resin printing also necessitates careful attention, particularly to ensure it is 100% cured. If a resin model isn’t fully cured, it may retain liquid resin internally, which could leak if the model breaks. Therefore, when opting for resin with food safety in mind, it’s critical to ensure complete curing. Rather than using a solid infill, opt for a hollow model with holes and cure the inner part using a small UV bulb. This method will help ensure the entire model, both externally and internally, is thoroughly cured and safe for contact with food.
The Final Word
The advent of 3D printing has undoubtedly brought along various challenges, including the issue of food safety. However, as the referenced study demonstrates, with the right cleaning protocols, we can confidently say that 3D printed objects are food safe for short-term use and dry storage.
As we continue to explore and innovate with 3D printing, it’s essential to maintain stringent safety standards, particularly for items in contact with food. But for now, rest assured that your 3D printed cookie cutters and utensils, when properly cleaned, can safely join your culinary adventures!
References:
https://lt728843.wixsite.com/maskrelief/post/the-final-say-in-food-safe-3d-printing
https://formlabs.com/asia/blog/guide-to-food-safe-3d-printing/

